Mathematical Modelling
METiS-USP – Morison Equation Time Domain Simulation
In-house code for the coupled analysis of offshore wind turbines capable of modeling the hydrodynamic loads on the hull (using a slender-body approach that considers first and second-order wave loads) and the aerodynamic loads on the rotor (with blade element momentum theory).
The performance of software has been compared to that of similar tools and verified against experimental results. The code is under constant development to improve its capabilities.
SuSSA – Subsea System Analysis
Analytical formulations for solving slender subsea structures associated to FOWT systems, such as mooring lines and umbilicals. Typical and innovative concepts can be assed, including shared mooring configurations.
The formulation was validated with experimental results and can be used for verification of high-order numerical simulations.


Floater-Moorings Optimisation Framework
To prospect potential uses for FOWTs and their application in site-specific scenarios, the TPN research group has developed a hull-mooring optimization framework that relies on parametric modelling of the hull geometry and mooring arrangement. The algorithm optimizes the FOWT dimensions based on the assessment of the system’s’ dynamics induced by wave, wind and currents. The environmental conditions are set-up in long-term data series, properly considering the correlations between the different environmental agents. The framework also performs costs estimations and checks whether the individuals created during the optimisation process meet the stability guidelines issued by classification societies.
EDTools – Engineering Design Tools
EDtools is an engineering solution developed in a partnership between Technomar Engenharia and TPN-USP to assist in the design and analysis of floating systems, with applications on floating wind as well. Edtools allows to model the main systems involved on FOWT technology (mooring systems, floater and turbine), and to easily compare several concepts, facilitating the validation and decision-making process.
EDtools also operates through a web interface with customization routines and as a management tool, integrating different industry software to optimize floating units and guarantee they will operate safely and with reduced cost.


SIL-USP – Software-in-the-loop
The research group has developed a dedicated controller to use the Software-in-the-Loop hybrid test approach. The software is able to estimate the wind turbine thrust in real-time, based on the measured motions of the platform, the mechanical properties of the wind turbine and the dynamic response of the generator. This allows to test the responses of FOWT during operational and parked conditions, to simulate emergency stops due to generator damages and to perform other norm-based tests.
Fluid Dynamics Simulaitons
CFD codes are used to asses the wind turbine performance, based on characterization of the FOWT wave-current induced motions and the aerodynamic loading. Time-domain simulations are also used to evaluate the interference effects between multiple FOWT in wind farm arrangements.

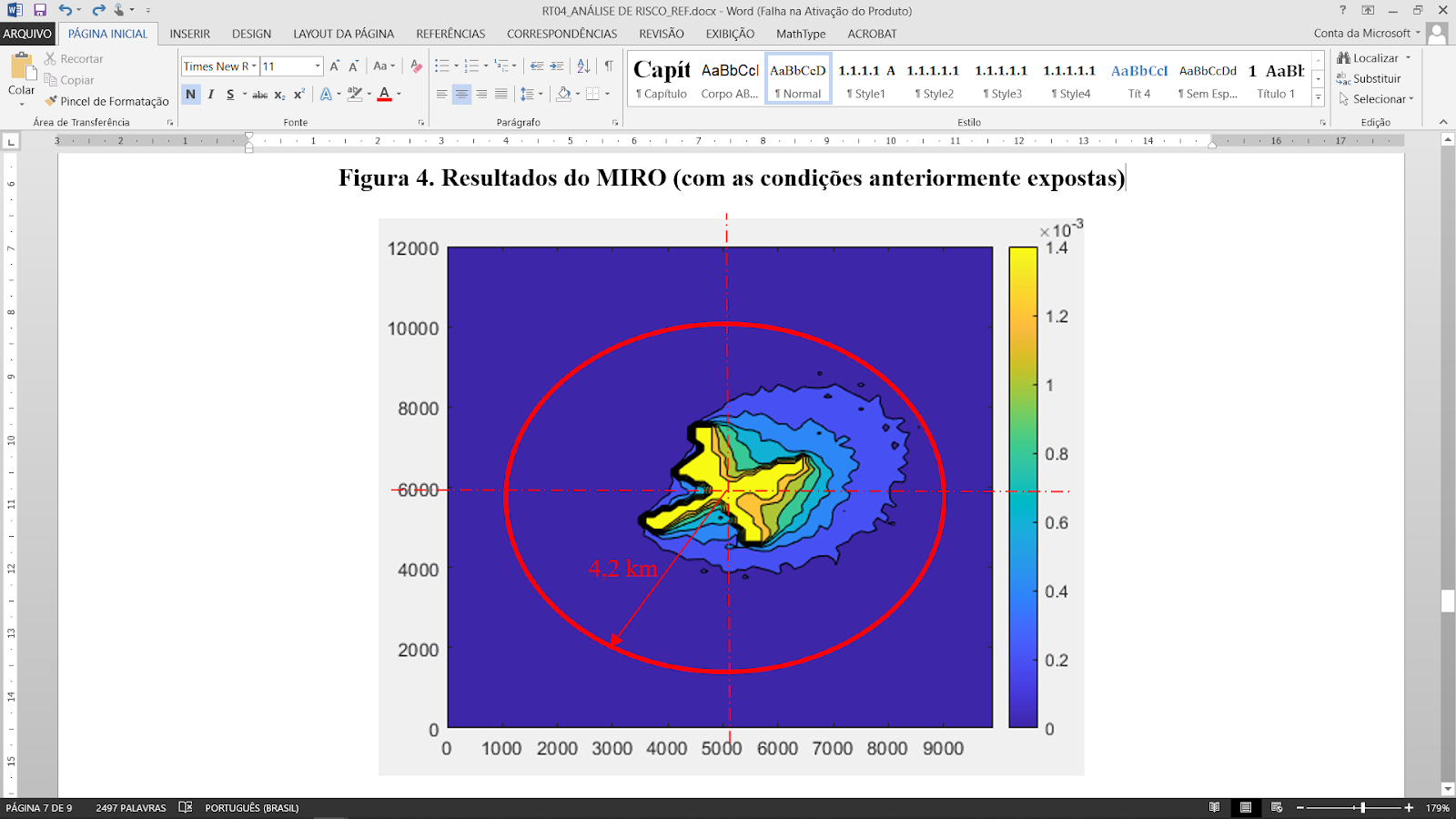

Risk and Reliability Analysis
State-of-the-art approaches are adopted to perform R&R assessments of FOWT designs for conventional and non-conventional applications, such as wind-to-oil systems. They also allow to estimate the expected downtime of particular configurations, as well as the variations in energy suplies due to preventive and corrective maintenance operations.
Structural Assessment
The structural behavior of the FOWT is assessed using Giraffe (an in-house software) and commercial packages. The wind turbine blades and the supporting tower are analyzed employing quasi-static or dynamic time domain models. The research group also develops models for the whole system combining finite element beams and rigid bodies, composing a rigid-flexible multibody model.




